0769-23388351
Toggle Navigation
Sintered neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) magnets, also commonly referred to as neodymium magnet, is currently the most commercially available permanent magnet material and is known as the "magnetic king". If you want to have a comprehensive understanding of it, just read this article.
Sintered ndfeb magnets are composed of three main elements: neodymium, iron, and boron, with the chemical formula Nd₂Fe₁₄B. They typically also contain dysprosium (Dy), terbium (Tb) to enhance coercivity and temperature stability, cobalt (Co) to increase the Curie temperature, and elements such as niobium (Nb), gallium (Ga), aluminum (Al), and copper (Cu) to improve microstructure and corrosion resistance. Its core manufacturing process is powder metallurgy, which primarily includes melting, powder production, shaping, sintering, heat treatment, mechanical processing, surface treatment, and electroplating.
Regarding the proportion of ingredients, please refer to: Main composition and proportion of rare earth neodymium magnets
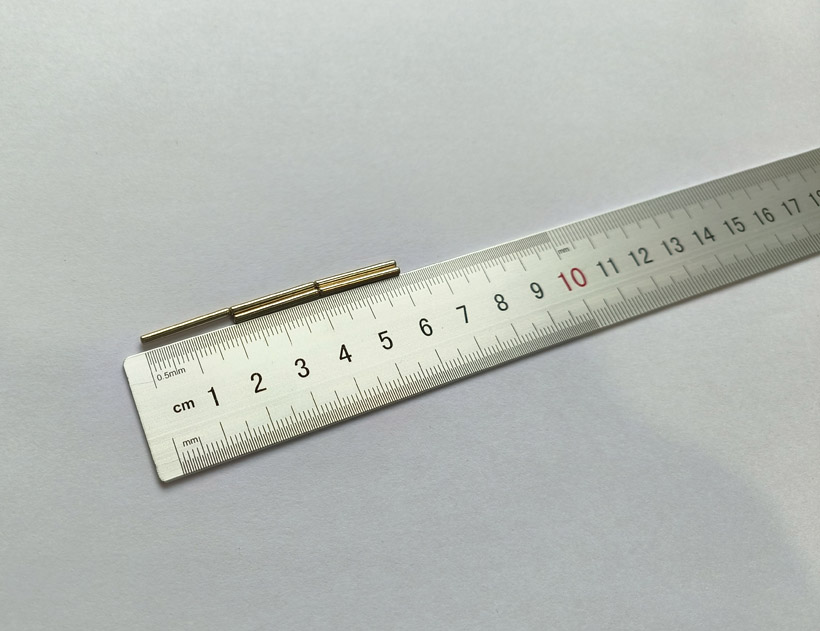
The picture shows 2x20mm neodymium cylindrical magnets.
The theoretical magnetic energy product of sintered ndfeb magnets can reach up to 64 MGOe, with current commercial products exceeding 54 MGOe, and residual magnetism exceeding 1.4 T. This means that under the same magnetic field strength, the volume can be made smaller, or a stronger magnetic field can be provided under the same volume.
Of course, it also has some drawbacks, such as relatively low Curie temperature, poor temperature stability, susceptibility to corrosion, and significant price volatility.
In terms of performance parameters and grades, the key magnetic performance parameters include remanence (the magnetic flux density when the external magnetic field is reduced to zero after the magnet is magnetized to saturation), coercivity, intrinsic coercivity, maximum magnetic energy product (representing the magnet's ability to store magnetic energy, which is the core indicator of comprehensive performance), squareness (the shape of the demagnetization curve, with a more rectangular shape being preferable), and recovery permeability.
For its grade designation, the international standard uses a “number + letter” naming convention (e.g., N52, N42SH, 48H). The number represents the maximum magnetic energy product that the magnet can achieve at room temperature, while the letter indicates the magnet's maximum operating temperature and intrinsic coercivity (Hcj) level.
Sintered ndfeb magnets leverage their high magnetic energy product and high power density to find widespread application in new energy vehicles, industrial motors, home appliances, various magnetic components, salvage equipment, medical instruments, magnetic levitation, acoustic equipment, smart communications, and more.
Currently, sintered ndfeb magnets dominate the permanent magnet market, accounting for the vast majority of the market share (far exceeding bonded neodymium-iron-boron magnets and hot-pressed/hot-deformed neodymium-iron-boron magnets). China is the world's largest producer, consumer, and exporter, accounting for more than 85-90% of global production. Japan and Europe also have a small amount of high-end production capacity.
Sintered NdFeB magnets are significantly stronger than aluminum-nickel-cobalt (AlNiCo) and ferrite magnets, particularly in high-performance motors and precision instruments. However, the main drawback of neodymium iron boron is its high brittleness, making it prone to demagnetization due to impact or high temperatures. As a result, AlNiCo or ferrite materials are more suitable for applications requiring high toughness or high-temperature resistance. AlNiCo has good high-temperature resistance and is suitable for applications in high-temperature environments, while ferrite, due to its low cost and weaker magnetic properties, is commonly used in low-end applications such as speakers and motors.
Similar articles;
Neodymium round magnets with a diameter of 5mm and a thickness of 4mm are more commonly used. If you feel that the magnetic force is not enough, the performance level can be appropriately improved. Welcome to consult the price!...
Our company is a permanent magnet supplier from China. We are good at processing micro-precision magnets, high-performance magnets, special-shaped magnets, and multi-pole ring magnets. The quality is guaranteed and the price is not expensive. We look forward to customer consultation from all over the world....
The sample is an N52 high-performance ultra small hole radially sintered neodymium rotor magnet, with specifications of 2mm outer diameter, 0.9mm bore, and 4.5mm height....
This is a square neodymium magnet for earphones, the length and width are 5mm, the thickness is 2mm, the thickness is magnetized, the surface is galvanized, 1mm or other thickness can also be selected, non-high temperature grade, the maximum working temperature is less than 80 ℃...
The sample is a high-performance ferrite rotor magnet with a radial 3-pair pole configuration (6 poles), measuring 20mm in outer diameter, center bore diameter of 8mm, and height of 27mm. surface magnetic flux density reaches approximately 1800 Gauss....
This is a small-sized short bar shaped neodymium iron boron strong magnet with a specification of 1.5 × 1.5 × 10mm. It is made of N42 performance grade neodymium iron boron material and magnetized along the length direction (10 mm direction)....
This is a rare earth NdFeB strong magnet with a length of 30mm, a width of 20mm and a thickness of 10mm. Surface treatment is nickel-copper-nickel, and the thickness is 10mm. Magnetization direction is length direction....
This product is a small rare earth NdFeB magnet ring, with gold plated surface, N52 grade, the magnetization method is axial, the size is 5mm outer diameter, 2mm inner hole, 2mm height, and the tolerance can be ±0.02mm. Welcome to consult us for the price....